https://docs.ceph.com/en/latest/cephadm/services
使用 systemctl 管理ceph 服务
- MON Service (Monitor Service):
- Monitors the health and status of the Ceph cluster.
- MGR Service (Manager Service):
- Overview: Provides a management interface for the Ceph cluster.
- OSD Service (Object Storage Daemon):
- Manages storage devices for storing and retrieving data as objects.
- RGW Service (RADOS Gateway Service – Object Gateway):
- Offers a RESTful API gateway interface for Ceph’s object storage.
- MDS Service (Metadata Server):
- Manages metadata for the Ceph File System (CephFS).
- NFS Service:
- Provides Network File System (NFS) access to Ceph storage.
- Utilizes the
nfs-ganeshadaemon.
- RBD Service (RADOS Block Device):
- Manages block storage devices within the Ceph cluster.
- Utilizes the
rbdcomponent and interacts with theradosandceph-osddaemons.
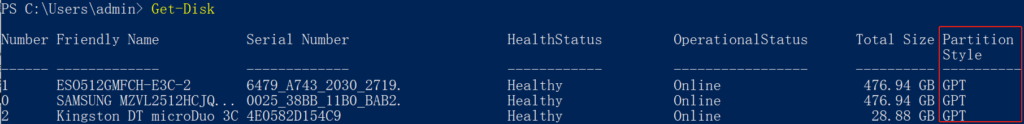
管理ceph服务级别
In a Ceph cluster, services are organized and managed at different levels:
- cluster
- node
- daemon
The command syntax to start, stop, or restart cluster service is;
ceph orch <start|stop|restart> <service_name>
List Ceph SystemD services running on a specific node;
sudo systemctl list-units "*ceph*"
Thus, the command syntax is;
ceph orch daemon <start|stop|restart> SERVICE_NAME
You can get the SERVICE_NAME from the ceph orch ps command.
ceph orch daemon restart grafana.ceph-admin
Check more on;
ceph orch daemon -h